
Senior Lecturer
Office : +603 7967 2061
Email : retnagowri@ummc.edu.my
UMExpert Link: https://umexpert.um.edu.my/rretnagowri
Publons Link: https://publons.com/researcher/2836046/retnagowri-rajandram/
Research Keywords : Cell death | Renal cell carcinoma | Translational medical research
Research Summary
Knockdown experiments exhibited Tumour necrosis factor Receptor Associated Factor -1’s (TRAF1) functional role in mediating apoptosis and suppressing mitosis in the cancer therapy-treated renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cell lines. In fact, TRAF1 was revealed to be a modulator of apoptosis in RCC. In recent work, TRAF1 expression knock down by siRNA in RCC cell line increased pro-survival c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 proteins while p65 knock down in RCC cell lines decreased levels of proliferation proteins, cyclin D1 and IL-6. Low TRAF1 in addition to high NF-κB p65 concentration in RCC tissue might cause increased cell proliferation and reduced apoptosis, inducing tumour growth. Future studies could include evaluating the effects of TRAF1 or p65 knock down on sensitivity to RCC targeted therapy drugs such as sunitinib, pazopanib or temsirolimus. Hence the possibility of improved diagnostic techniques and development of new therapies for RCCs using these modulators does hold some promise.
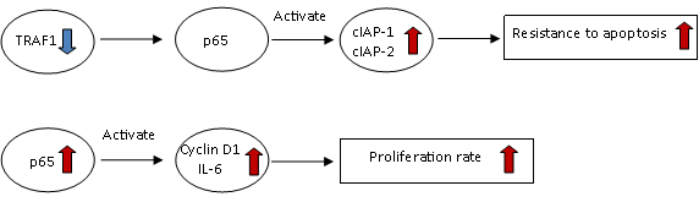
Diagram depicted from Dr. Yap Ning Yi’s thesis published in 2018
Dr Retnagowri’s research revolves around the investigation of the underlying mechanism of cell death pathway using a cell and molecular biology methods, in addition to, translational research crosstalk with renal cell carcinoma clinical experts. Deciphering the role and function of the apoptotic pathway and other related pathways may potentially delivers avenues for new treatment targets and biomarker discovery for renal cell carcinoma. In turn holds the capacity for early and curative measures for the disease and potentially prolonged and improved quality of life for renal cell carcinoma burdened patients.
Main Research Interest / Goals
- Marker discovery in Renal Cell Carcinoma; such as TRAF1, NF-κB: Leptin and its receptor, ICAD, as well as clinical indicators
- Establishment and characterization of Malaysian renal cell carcinoma cell lines
- Molecular Profiling And Pathway Analysis Of Clinically Aggressive Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Translational crosstalk for Renal Cell Carcinoma for early detection and creating platform for treatment regimen for this disease
Selected Publications
- Yap, N. Y., Ng, K. L., Ong, T. A., Pailoor, J., Gobe, G. C., Ooi, C. C., . . . Rajandram, R. (2013). Clinical prognostic factors and survival outcome in renal cell carcinoma patients–a malaysian single centre perspective. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 14(12), 7497-7500.
- Rajandram, R., Yap, N. Y., Pailoor, J., Razack, A. H., Ng, K. L., Ong, T. A., . . . Gobe, G. C. (2014). Tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-1 (TRAF-1) expression is increased in renal cell carcinoma patient serum but decreased in cancer tissue compared with normal: potential biomarker significance. Pathology, 46(6), 518-522.
- Yap, N. Y., Ong, T. A., Morais, C., Pailoor, J., Gobe, G. C., & Rajandram, R. (2019). Establishment of epithelial and fibroblast cell cultures and cell lines from primary renal cancer nephrectomies. Cell Biol Int, 43(6), 715-725.
- Rajandram, R., Perumal, K., & Yap, N. Y. (2019). Prognostic biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma: is there a relationship with obesity? Transl Androl Urol, 8(Suppl 2), S138-S146.
- Yap, N. Y., Yap, F. N., Perumal, K., & Rajandram, R. (2019). Circulating adiponectin as a biomarker in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomarkers, 24(6), 607-614.

